Computes the linear covariance function: $$k(s, t) = \sigma^2 (s - c)(t - c)$$
Details
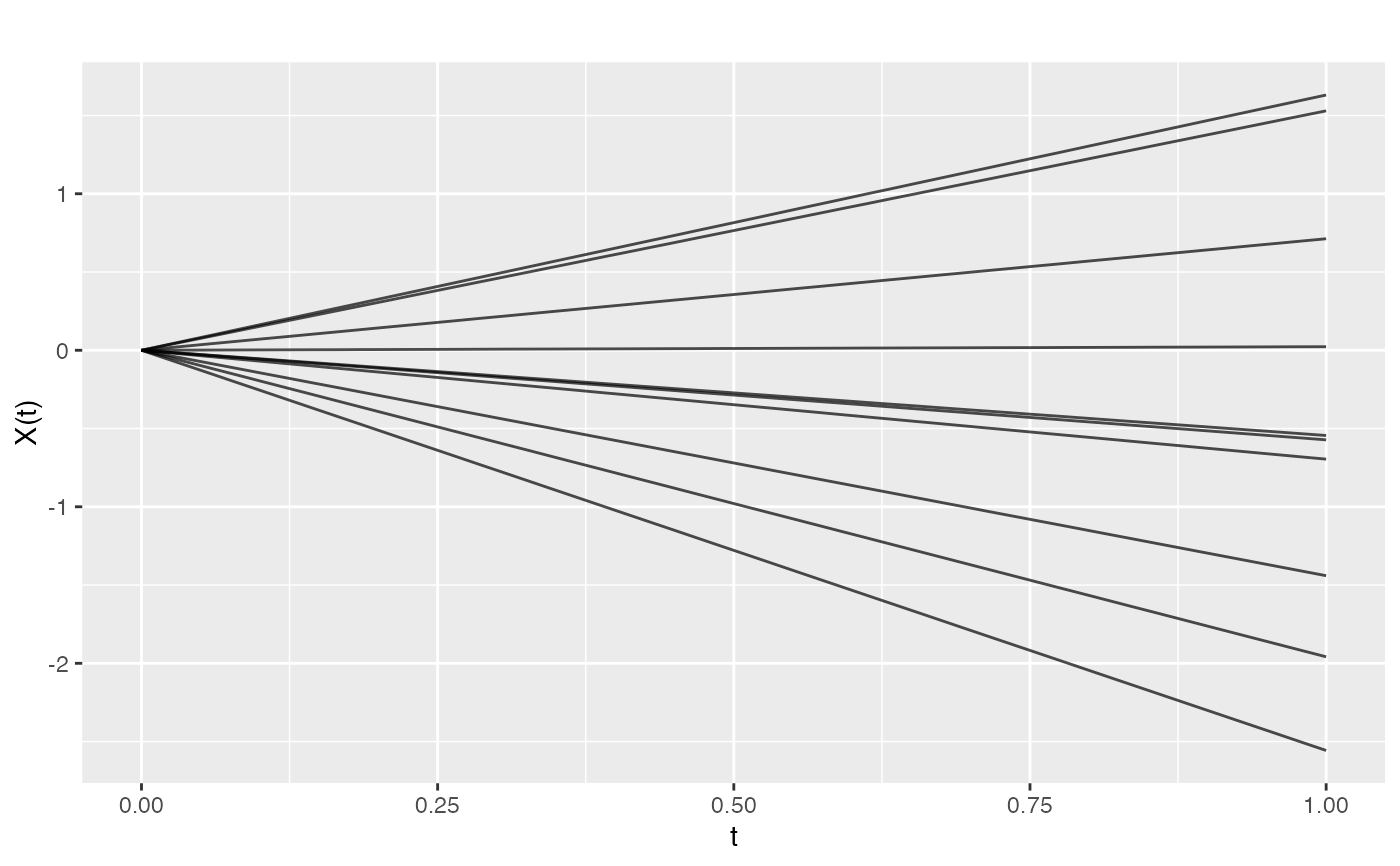
The linear covariance function produces sample paths that are linear functions. It is useful when the underlying process is expected to have a linear trend.
Examples
# Generate linear function samples
cov_func <- kernel.linear(variance = 1)
t <- seq(0, 1, length.out = 50)
fd <- make.gaussian.process(n = 10, t = t, cov = cov_func)
plot(fd)