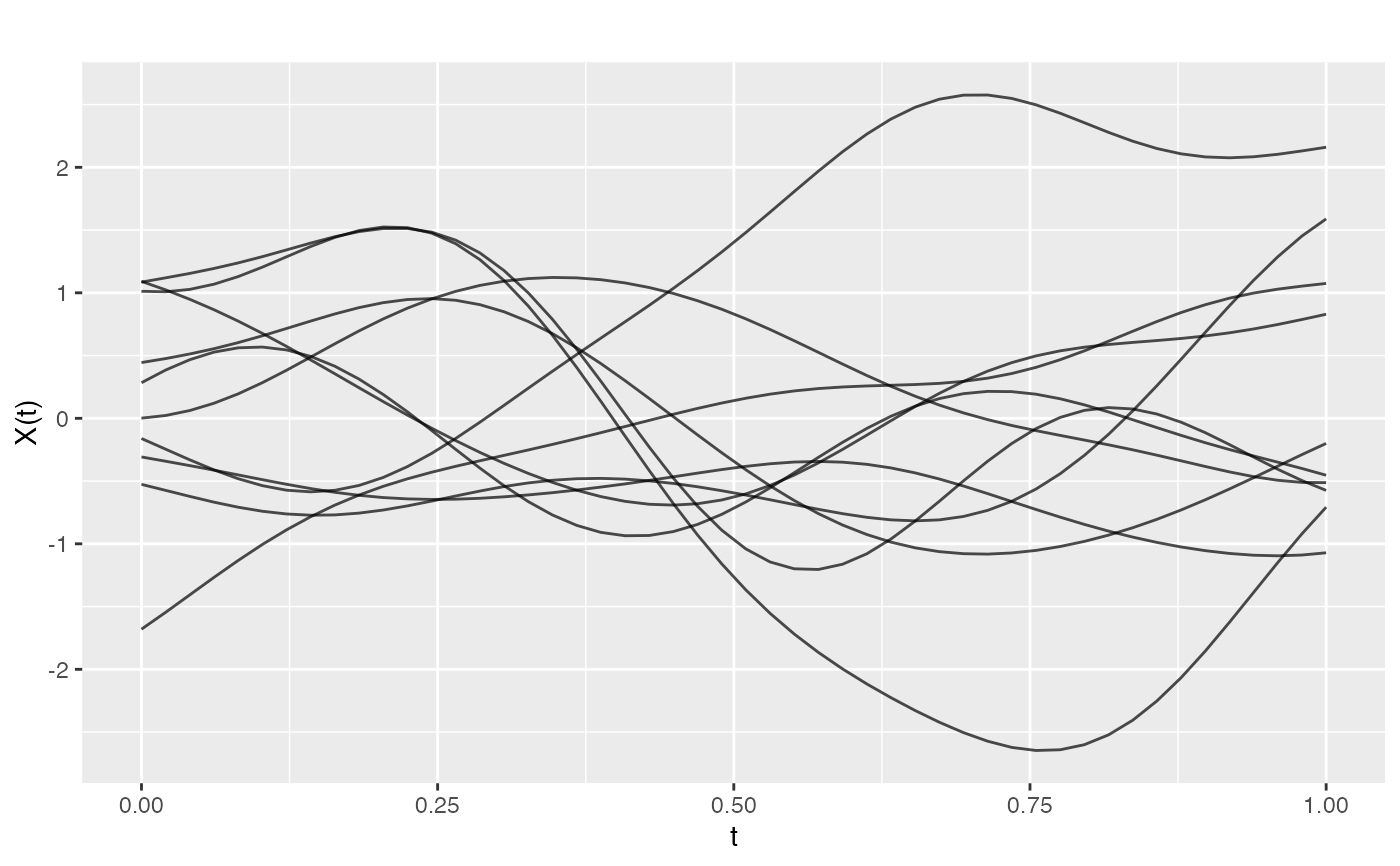
Computes the Gaussian (RBF/squared exponential) covariance function: $$k(s, t) = \sigma^2 \exp\left(-\frac{(s-t)^2}{2\ell^2}\right)$$
Details
This kernel produces infinitely differentiable (very smooth) sample paths.
The Gaussian covariance function, also known as the squared exponential or radial basis function (RBF) kernel, is one of the most commonly used covariance functions. It produces very smooth sample paths because it is infinitely differentiable.
The length scale parameter controls how quickly the correlation decays with distance. Larger values produce smoother, more slowly varying functions.
Examples
# Create a Gaussian covariance function
cov_func <- kernel.gaussian(variance = 1, length_scale = 0.2)
# Evaluate covariance matrix on a grid
t <- seq(0, 1, length.out = 50)
K <- cov_func(t)
image(K, main = "Gaussian Covariance Matrix")
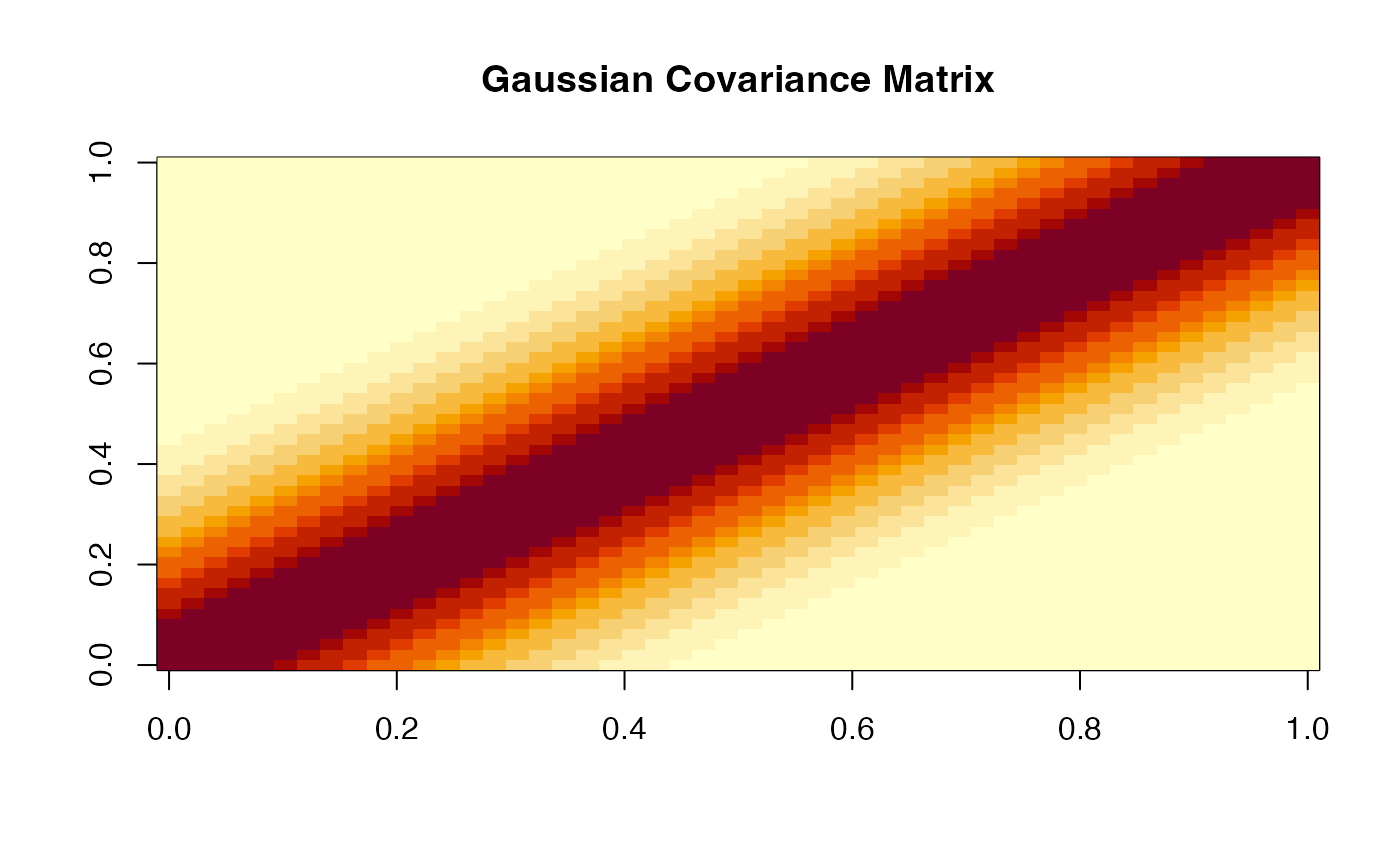 # Generate Gaussian process samples
fd <- make.gaussian.process(n = 10, t = t, cov = cov_func)
plot(fd)
# Generate Gaussian process samples
fd <- make.gaussian.process(n = 10, t = t, cov = cov_func)
plot(fd)